Virtualization has revolutionized how we use computers, allowing us to create multiple virtual machines that run different operating systems and applications on a single physical server. Whether you’re a home lab hobbyist or an IT professional, virtualization is a crucial concept you’ll want to be familiar with. It’s the foundation of modern computing infrastructure, allowing virtual environments to be entirely separate from the physical hardware that runs them. In this post, we’ll explore the basics of virtualization, including what it is, why it’s essential, and how it’s implemented in both home lab and enterprise environments. We’ll also take a closer look at the various virtualization software options available, including type 1 and type 2 hypervisors, and discuss the pros and cons of each. So whether you’re entirely new to virtualization or looking to deepen your understanding of this critical technology, read on to learn everything you need.
What is Virtualization?
At its core, virtualization is a method of running multiple operating systems on a single physical machine. It creates a layer of abstraction between the physical hardware and the operating system, allowing multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run independently on the same physical server. This abstraction layer is created by a software program called a hypervisor, which creates and manages the VMs that run independently on the same physical server. Each VM runs its operating system and applications as if running on a separate physical machine. This allows multiple VMs to share the resources of a single physical device, such as CPU, memory, and storage, while maintaining isolation.
The concept of virtualization is not new, but it has become increasingly popular in recent years due to the growth of cloud computing, big data, and the need to consolidate resources to save costs. The first virtual machine was created in the 1960s by IBM, and virtualization technology has evolved significantly since then. Virtualization has revolutionized the IT industry by enabling businesses to run multiple applications and operating systems on a single server. This has dramatically improved resource utilization, simplified management, and reduced costs.
Although widely used in enterprise environments, virtualization is easily achievable at home. With low-cost and free virtualization software, such as VirtualBox, VMware Player, and Hyper-V, anyone can create and manage virtual machines on a personal computer. This allows one to experiment with different operating systems, applications, and configurations without investing in additional physical hardware. Furthermore, with the advent of cloud-based services, renting virtual machines on a pay-as-you-go basis is possible, giving even more flexibility and scalability to home lab setups. The accessibility of virtualization technology means that it is a valuable tool for hobbyists, students, and professionals alike, regardless of their technical expertise or budget level.
Types of Hypervisors
There are two types of hypervisors, Type 1 and Type 2, which differ in their architecture and use cases.
Type 1 Hypervisor
A Type 1 hypervisor, or a native or bare-metal hypervisor, runs directly on the host system’s hardware. It is installed and configured on the physical machine, and virtual machines run on top of it. Type 1 hypervisors are designed for enterprise-level virtualization and are used to consolidate multiple physical servers into a single virtual server.
One of the significant advantages of Type 1 hypervisors is that they have direct access to the hardware, which makes them more efficient and faster than Type 2 hypervisors. They can also provide a high level of isolation between virtual machines, which enhances security. However, setting up a Type 1 hypervisor can be complicated and requires some technical expertise.
Type 2 Hypervisor
A Type 2 hypervisor, also known as a hosted hypervisor, runs on top of a host operating system like any other application. It is installed and configured on the host system, and virtual machines run on top of it. Type 2 hypervisors are designed for personal and small-scale virtualization and are used to run multiple operating systems on a single machine.
One of the significant advantages of Type 2 hypervisors is that they are easy to install and use, making them ideal for beginners. They can also be used on various hardware, including desktops, laptops, and servers. However, they are less efficient and slower than Type 1 hypervisors since they must share resources with the host operating system.
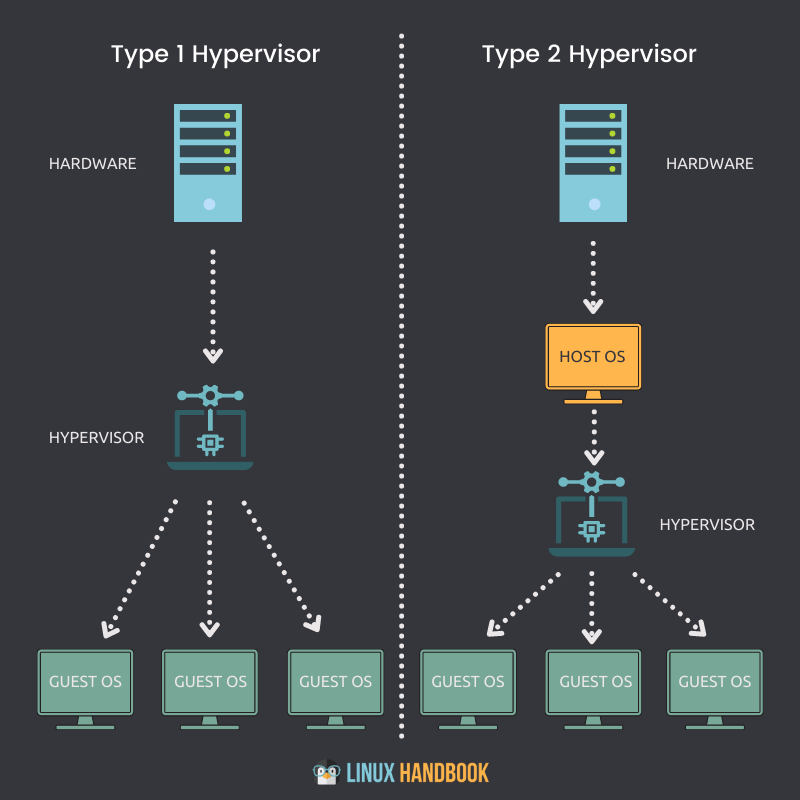
The choice between Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors depends on the use case. If you’re an enterprise looking to consolidate multiple physical servers into a single virtual server, Type 1 hypervisors are the way to go. If you’re looking to run multiple operating systems on a single machine, Type 2 hypervisors are more suitable.

Popular Virtualization Software
Many virtualization software options are available, both type 1 and type 2 hypervisors, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are some of the most popular virtualization software options available:
- VMware ESXi: VMware ESXi is a Type 1 hypervisor designed for enterprise-level virtualization. It is installed directly on the physical server, and virtual machines run on top of it. ESXi is known for its reliability, performance, and scalability, making it an excellent choice for large-scale virtualization environments. Many large enterprises use VMware ESXi because of its advanced features, such as vMotion, which allows virtual machines to be moved between physical servers without downtime. It also has excellent security features, such as VM Encryption and Secure Boot, which help keep virtual machines secure.
- Microsoft Hyper-V: Microsoft Hyper-V is a Type 1 hypervisor with Windows Server. It is designed for enterprise-level virtualization and can consolidate multiple physical servers into one virtual server. Hyper-V supports various operating systems and applications, making it a versatile virtualization option. Hyper-V also includes advanced features such as live migration, which allows virtual machines to be moved between physical servers with minimal downtime, and Hyper-V Replica, which provides disaster recovery capabilities.
- Oracle VirtualBox: Oracle VirtualBox is a Type 2 hypervisor designed for personal and small-scale virtualization. It can be installed on any host operating system and run multiple operating systems on a single machine. VirtualBox is free and easy to use, making it an excellent option for beginners. It supports various guest operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. VirtualBox also includes advanced features such as snapshotting, which allows users to save a virtual machine’s state and revert to it if necessary.
- VMware Workstation: VMware Workstation is a Type 2 hypervisor designed for personal and small-scale virtualization. It can be installed on any host operating system and run multiple operating systems on a single machine. Workstation offers advanced features such as snapshotting and cloning, making it an excellent option for software developers and testers. It also includes features such as network simulation, which allows users to test network configurations in a virtual environment.
- Parallels Desktop: Parallels Desktop is a Type 2 hypervisor for Mac users. It can run Windows and other operating systems on a Mac. Parallels Desktop offers advanced features such as Coherence mode, which allows users to run Windows applications seamlessly on a Mac. It also includes features such as One-Click tuning, which optimizes virtual machines for specific gaming or software development tasks.
Overall, the differences between these virtualization software options lie in their specific use cases, level of complexity, and cost. Enterprises typically opt for Type 1 hypervisors such as VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V due to their robust features, security, and scalability. Meanwhile, individuals and small businesses often prefer Type 2 hypervisors such as Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, and Parallels Desktop due to their ease of use, versatility, and affordability.

Virtualization in Business or Home Environments
Virtualization is a versatile technology used in various environments, from large-scale enterprise data centers to small home offices. In business environments, virtualization is commonly used to consolidate physical servers, reduce IT infrastructure costs, and increase efficiency. Virtualization allows multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server, which reduces the need for additional hardware and improves resource utilization. It also enables IT administrators to easily manage and monitor virtual servers, perform backups and restores, and create disaster recovery plans.
In home environments, virtualization can be used for a variety of purposes. For example, it can run multiple operating systems on a single machine, allowing users to experiment with different software and configurations without affecting their primary operating system. Virtualization can also be used to run applications that may not be compatible with a user’s primary operating system, such as running Windows applications on a Mac. Additionally, virtualization can create a sandbox environment for testing potentially harmful software or malware, protecting the host system from potential damage.
Overall, the benefits of virtualization in both business and home environments include cost savings, increased efficiency, improved resource utilization, and greater flexibility. Users can take advantage of the benefits of multiple operating systems and applications without additional hardware or software by virtualizing servers and applications. Virtualization is a powerful technology that can be used in various ways to improve IT infrastructure and increase productivity in the workplace and at home.
Wrapping Up
Virtualization is a powerful technology that has transformed the IT landscape. It allows users to consolidate servers, increase efficiency, and reduce costs, making it a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes. Furthermore, virtualization can be utilized in personal projects, providing users with greater flexibility and the ability to experiment with different operating systems and applications.
There are two types of hypervisors – Type 1 and Type 2 – each with strengths and weaknesses. Type 1 hypervisors are more powerful and efficient, making them ideal for enterprise environments, while Type 2 hypervisors are easier to install and use, making them a popular choice for personal projects.
Several popular virtualization software options are available, including VMware, Hyper-V, VirtualBox, Workstation, and Parallels, each with unique features and capabilities. Users should choose the software that best fits their needs and goals.
Finally, virtualization can be used in both business and home environments, providing users with cost savings, increased efficiency, and greater flexibility. Whether you want to consolidate servers, experiment with different operating systems, or protect your system from malware, virtualization is a powerful tool to help you achieve your goals.
Overall, virtualization is a game-changing technology that has revolutionized the IT industry. As virtualization evolves, it will become even more important and ubiquitous, making it an essential skill for IT professionals and enthusiasts.

About Home Lab Mentor
Home Lab Mentor is dedicated to educating individuals of all skill levels in various IT projects with a focus on home labs.
Newsletter
Subscribe to the email newsletter to gain updates on new posts and projects.
